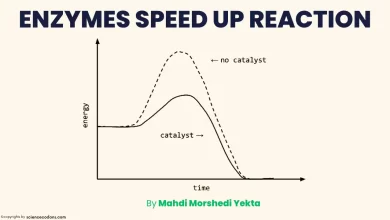
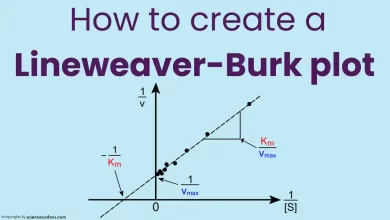
Km and Kcat are important parameters describing the kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. They are derived from the Michaelis-Menten equation, which relates the reaction rate (v) to the enzyme concentration ([E]) and the substrate concentration ([S]):
$$v = \frac{k_{cat}[E][S]}{K_m + [S]}$$
Km is the Michaelis constant, which represents the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of the maximum rate (Vmax). It measures the enzyme’s affinity for the substrate: the lower the Km, the higher the affinity. Km can be calculated from the rate constants of the enzyme-substrate complex formation (k1) and dissociation (k-1) and the product formation (kcat):
$$K_m = \frac{k_{-1} + k_{cat}}{k_1}$$
- Measured in molarity (M), which represents the concentration of substrate.
Kcat is the turnover number, representing the number of substrate molecules converted to product per enzyme molecule per unit of time when the enzyme is fully saturated with substrate. It measures the enzyme’s catalytic efficiency: the higher the Kcat, the faster the reaction. Kcat equation: Kcat is equal to Vmax divided by the total enzyme concentration:
$$k_{cat} = \frac{V_{max}}{[E]}$$
- Measured in units per second (s⁻¹) or reactions per second (s⁻¹).
| Feature | kcat | Km |
|---|---|---|
| What it measures | Maximum reaction rate | Substrate affinity |
| Units | s-1 | M |
| Interpretation | Higher value = faster enzyme | Lower value = higher affinity |
| Analogy | Factory worker speed | Finding a specific book in a library |
The ratio of Kcat to Km is also known as the specificity constant, which represents the reaction rate when the substrate concentration is very low compared to Km. It measures the enzyme’s overall efficiency: the higher the Kcat/Km, the more efficient the enzyme. The specificity constant can be used to compare the preference of an enzyme for different substrates or the performance of different enzymes for the same substrate.
Example
Let’s consider an example of two enzymes, A and B, that catalyze the same reaction with different substrates, X and Y. The following table shows the values of Km and Kcat for each enzyme-substrate pair:
| Enzyme | Substrate | Km (M) | Kcat (s^-1^) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | X | 0.01 | 100 |
| A | Y | 0.1 | 50 |
| B | X | 0.001 | 10 |
| B | Y | 0.01 | 20 |
We can calculate the specificity constants for each enzyme-substrate pair by dividing Kcat by Km:
| Enzyme | Substrate | Kcat/Km (M^-1^s^-1^) |
|---|---|---|
| A | X | 10,000 |
| A | Y | 500 |
| B | X | 10,000 |
| B | Y | 2,000 |
From the table, we can see that:
- Enzyme A has a higher affinity for substrate X than substrate Y, as indicated by the lower Km value.
- Enzyme A has a higher catalytic efficiency for substrate X than substrate Y, as indicated by the higher Kcat value.
- Enzyme A has a higher overall efficiency for substrate X than substrate Y, as indicated by the higher Kcat/Km value.
- Enzyme B has a higher affinity for both substrates than enzyme A, as indicated by the lower Km values.
- Enzyme B has a lower catalytic efficiency for both substrates than enzyme A, as indicated by the lower Kcat values.
- Enzyme B has the same overall efficiency for substrate X as enzyme A but a lower overall efficiency for substrate Y, as indicated by the Kcat/Km values.
Therefore, we can conclude that:
- Enzyme A is more specific for substrate X than for substrate Y.
- Enzyme B is less specific for both substrates than enzyme A but more specific for substrate Y than for substrate X.
- Enzymes A and B have the same specificity for substrate X, but enzyme A is more typical for substrate Y than enzyme B.
summary
kcat tells you how fast an enzyme can work when it’s got all the substrate it needs, while Km tells you how easily it can find and grab that substrate in the first place. Both are important for understanding how enzymes function and how they are adapted to their specific roles in cells.