ALL types of mutations are:
Substitution Mutation :
A substitution mutation occurs when one nucleotide is replaced by another in the DNA sequence. This type of mutation can be further classified into three subtypes:
a. Silent Mutation: When the substitution does not result in any change in the amino acid sequence due to the degeneracy of the genetic code.
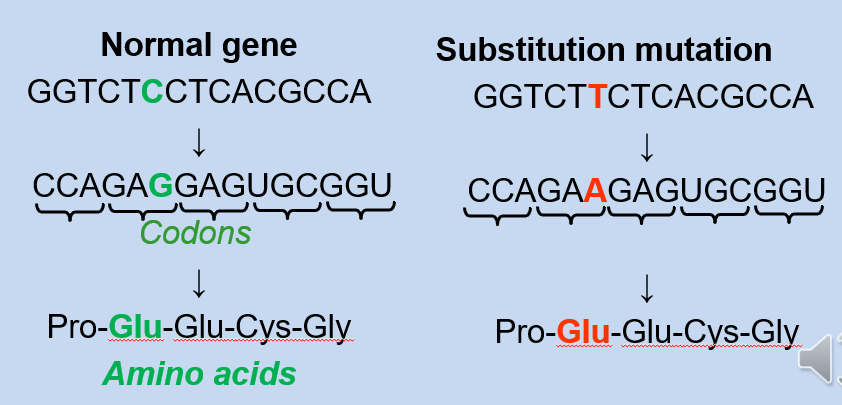
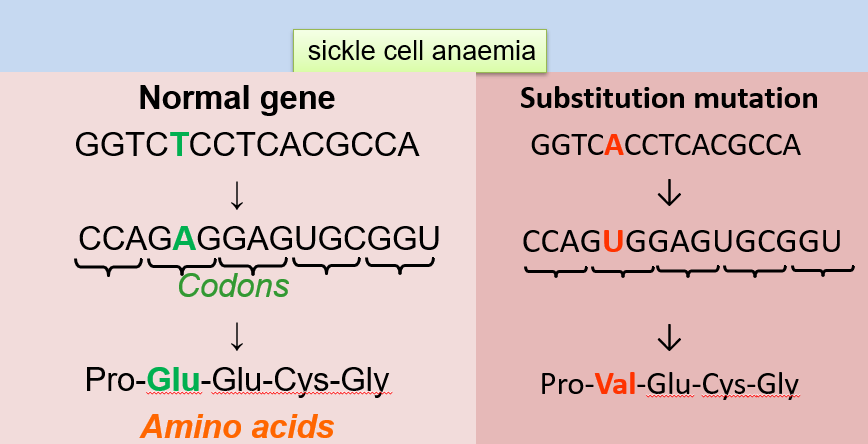
b. Missense Mutation: When the substitution leads to incorporating a different amino acid in the protein sequence, potentially altering its structure and function.
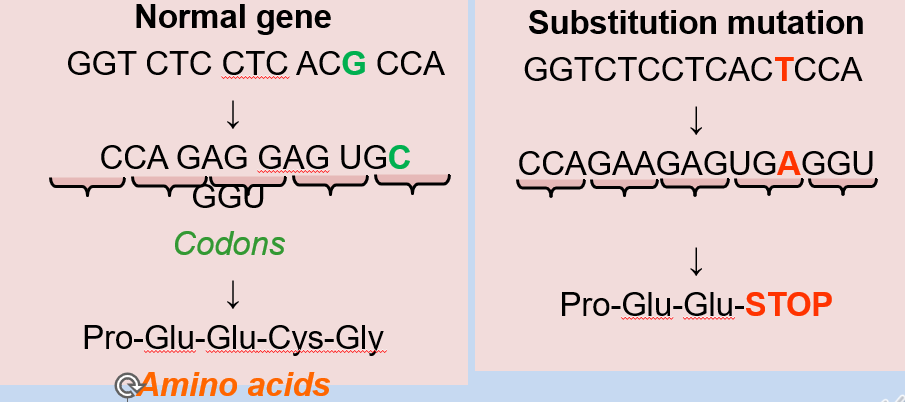
c. Nonsense Mutation: When the substitution introduces a premature stop codon, resulting in the production of a truncated protein.
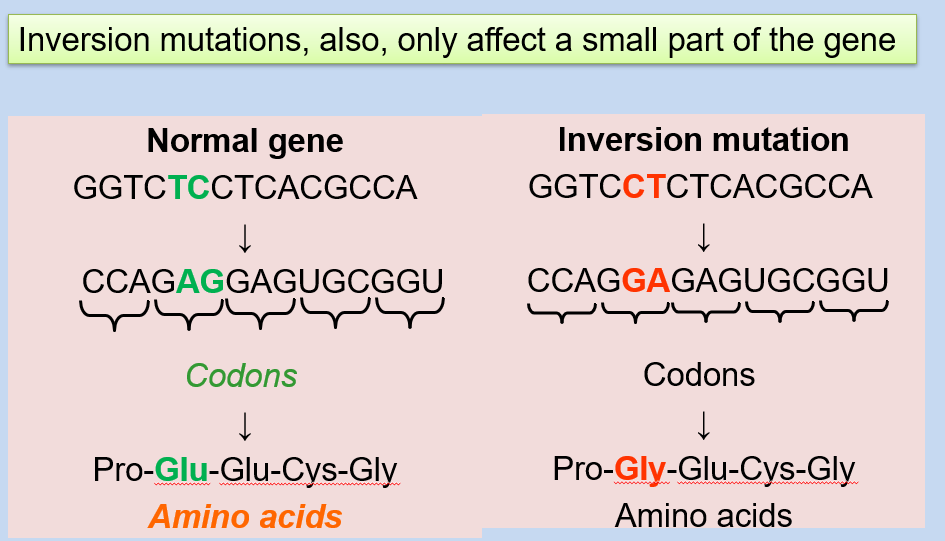
d. Inversion mutations
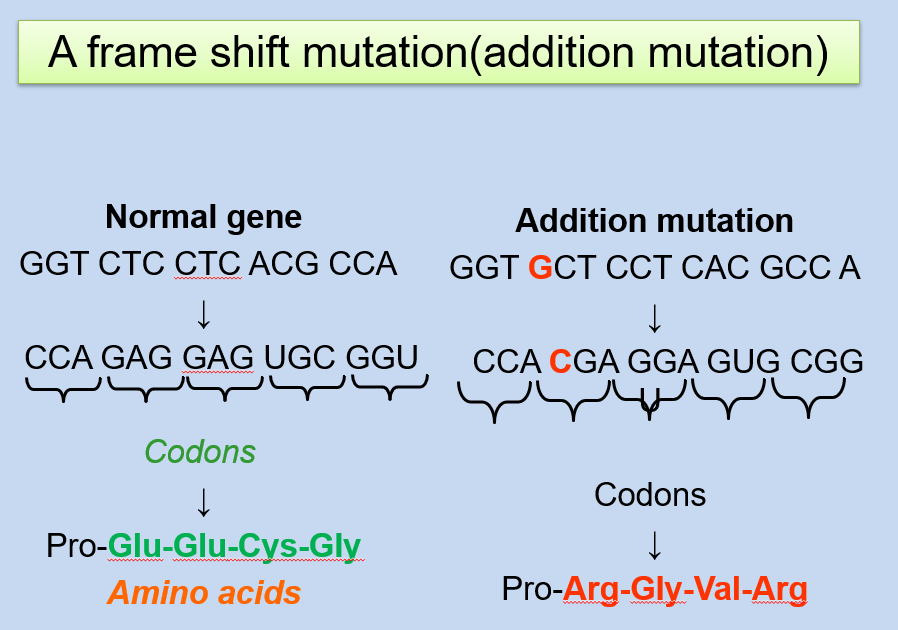
Frameshift Mutation
Frameshift mutations occur when nucleotides are inserted or deleted in a number that is not a multiple of three. As a result, the reading frame of the DNA sequence is shifted, leading to a completely different amino acid sequence downstream of the mutation site. Frameshift mutations frequently lead to non-functional proteins because they cause significant changes to the protein’s primary structure.
Insertion Mutation: An insertion mutation involves the addition of one or more nucleotides into the DNA sequence. This can lead to a shift in the reading frame during translation, causing a significant change in the resulting protein structure and function.
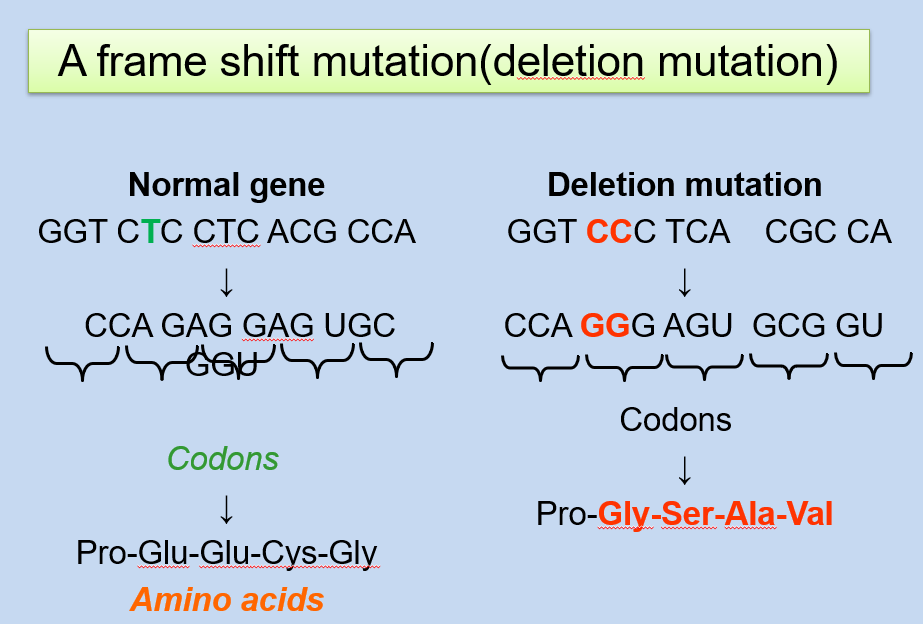
Deletion Mutation: A deletion mutation is the removal of one or more nucleotides from the DNA sequence. Deletions (like insertion mutations) can cause a shift in the reading frame and result in a different protein sequence and potentially a non-functional protein.
conclusion
These four types of mutations can occur spontaneously or be induced by various factors, such as errors during DNA replication, exposure to mutagenic agents (such as radiation or certain chemicals), or genetic recombination events. Mutations play a significant role in genetic diversity and can have both harmful and beneficial effects on organisms.
| Mutation Type | Description | Effect on Protein |
|---|---|---|
| Substitution | Another replaces one nucleotide | – Silent: No change in amino acid sequence. – Missense: Different amino acids incorporated, potentially altering protein structure and function. – Nonsense: Premature stop codon, resulting in a truncated protein. |
| Insertion | Addition of one or more nucleotides into the DNA sequence. | Shift in the reading frame during translation, leading to significant changes in the resulting protein sequence and structure. |
| Deletion | Removal of one or more nucleotides from the DNA sequence. | Shift in the reading frame during translation, causing changes in the resulting protein sequence and structure. |
| Frameshift | Insertion or deletion of nucleotides not in multiples of three. | Shift in the reading frame during translation, resulting in a completely different amino acid sequence downstream of the mutation site. Often leads to non-functional proteins. |