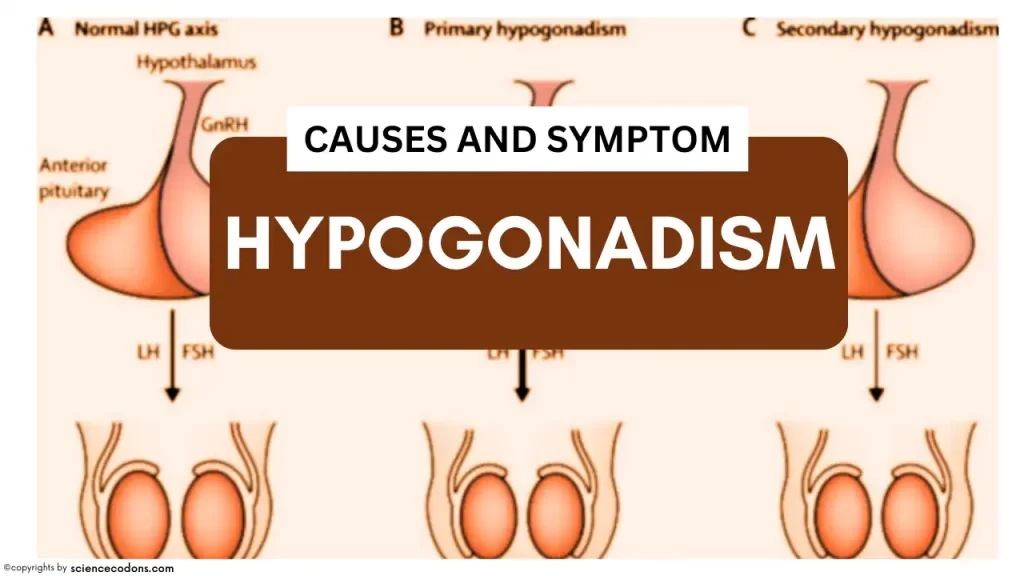
Hypogonadism is a fascinating subject in the field of endocrinology. It is a disorder characterized by the body’s inability to produce sufficient amounts of sex hormones and impairing the spermatogenesis process, leading to a variety of symptoms and complications. The causes of hypogonadism are as diverse as the condition itself, falling into two main categories: primary and central hypogonadism.
| Type | Causes |
|---|---|
| Primary Hypogonadism | Genetic disorders (Klinefelter syndrome, Turner syndrome), Kidney and liver diseases, Exposure to radiation, Surgery on the sex organs, Autoimmune disorders (Addison’s disease), Hemochromatosis |
| Central Hypogonadism | Genetic disorders (Kallmann syndrome), HIV and AIDS infections, Rapid weight loss, Nutritional deficiencies, Brain Surgery, Radiation Exposure, Tumor in or near the pituitary glands |
let’s talk more…
1-Kallmann syndrome: This type of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism occurs due to a defect in the migration of GnRH neurons from the olfactory placode to the hypothalamus. Complete or partial olfactory problems characterize it. A deficiency in GnRH characterizes this syndrome. These patients have small testes and may become infertile.
2- Hyperprolactinemia: Increased prolactin reduces GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone)secretion and reduces LH’s (luteinizing hormone) effect on Leydig cells. Additionally, it diminishes the impact of testosterone on target cells, resulting in a condition known as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.
3-Weight loss: Losing a lot of weight reduces the release of GnRH and the levels of gonadotropin and testosterone, leading to secondary hypogonadism. This condition is seen in patients with cancer, AIDS, and chronic inflammation.
4- Klinefelter syndrome: These individuals have an XXY phenotype. Clinical manifestations of this disease include hypogonadism, gynecomastia, small testes (less than 2 centimeters), azoospermia, a feminine appearance, and increased LH and FSH.
5- Cryptorchidism: About 3% of male newborns have cryptorchidism. When the testes are not appropriately descended and remain inside the abdomen, it can lead to a deficiency in spermatogenesis and oligospermia. Leydig cells and testosterone levels are normal in these patients.
6- Acquired failure: Infection with mumps, gonorrhea, orchitis, radiation, vascular injury, trauma, alcohol consumption, and chemotherapy are seen. The serum concentration of FSH may be normal or elevated. Testicular function may decline with age in some men. In individuals with decreased testosterone secretion, there is a decline in strength and sexual desire, as well as feelings of instability, fatigue, and signs of exhaustion. In these conditions, LH levels rise.
7- Testicular feminization: The lack of androgen receptors causes false hermaphroditism in these patients. The labial-scrotal fold does not fuse, the vagina is short, the testes are small and located inside the abdomen, and there are no fallopian tubes or upper part of the uterus. These patients experience gynecomastia during puberty as a result of decreased estradiol secretion and increased conversion of testosterone to estrogens in the environment. Axillary and pubic hair does not grow. The patients have high concentrations of testosterone because LH is constantly stimulating it, and LH concentrations are high because testosterone is unable to affect the hypothalamus.
8- 5-alpha reductase deficiency is a condition where the enzyme responsible for converting testosterone to DHT is lacking. In these patients, the urethral opening is located on the body of the genital organ. During puberty, the production of androgens is sufficient to compensate for any relative deficiencies, allowing for physiological growth in males. The scrotum and phallus usually develop.
To examine these individuals, tests should be conducted for FSH, LH, and semen analysis. If LH, FSH, and testosterone levels are low, it may indicate hypothalamic-pituitary disorders. After this discovery, prolactin and imaging studies should be conducted. High concentrations of LH and FSH, along with low testosterone levels, indicate a primary deficiency in the testes. If the testicle is not located within the scrotum, an HCG stimulation test should be conducted. An increase in testosterone levels in this test indicates the presence of testicular activity.
Hypogonadism(Low Testosterone) Symptoms
In hypogonadism, there is a decrease in testosterone and estrogen levels. Clinical manifestations depend heavily on the severity and timing of the deficiency.
- Hypogonadism during fetal development can lead to ambiguous genitalia and pseudohermaphroditism in males.
- Hypogonadism at the end of pregnancy can result in the absence of testes in the scrotum, either unilaterally or bilaterally, as well as cryptorchidism.
- Before puberty, it can cause decreased muscle strength, weak muscles, a high-pitched voice, decreased axillary and pubic hair, and a deficiency in facial hair. The long bones of the limbs and arms continue to grow under the influence of growth hormones, developing masculine physical characteristics.
- After puberty, hypogonadism can lead to a decrease in libido, sexual dysfunction, low energy levels, fine lines around the eyes and mouth, and reduced facial and body hair.
| Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Decreased sex drive | A reduced desire for sexual activity |
| Decreased energy | Feeling tired or fatigued |
| Depression | Persistent feelings of sadness or loss of interest |
| Erectile dysfunction | Difficulty getting or maintaining an erection |
| Infertility | Difficulty in achieving pregnancy |
| Decrease in hair growth | Reduced hair growth on the face and body |
| Decrease in muscle mass | Loss of muscle bulk |
| Development of breast tissue (gynecomastia) | Enlargement of breast tissue in males |
| Loss of bone mass (osteoporosis) | Weakening of bones |