Yes, DNA strands are antiparallel. In a DNA molecule, two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between their nitrogenous bases. The two strands run in opposite directions, meaning they have opposite orientations. One strand runs in the 5′ to 3′ direction, while the other runs in the 3′ to 5′ direction. This arrangement is referred to as antiparallel.
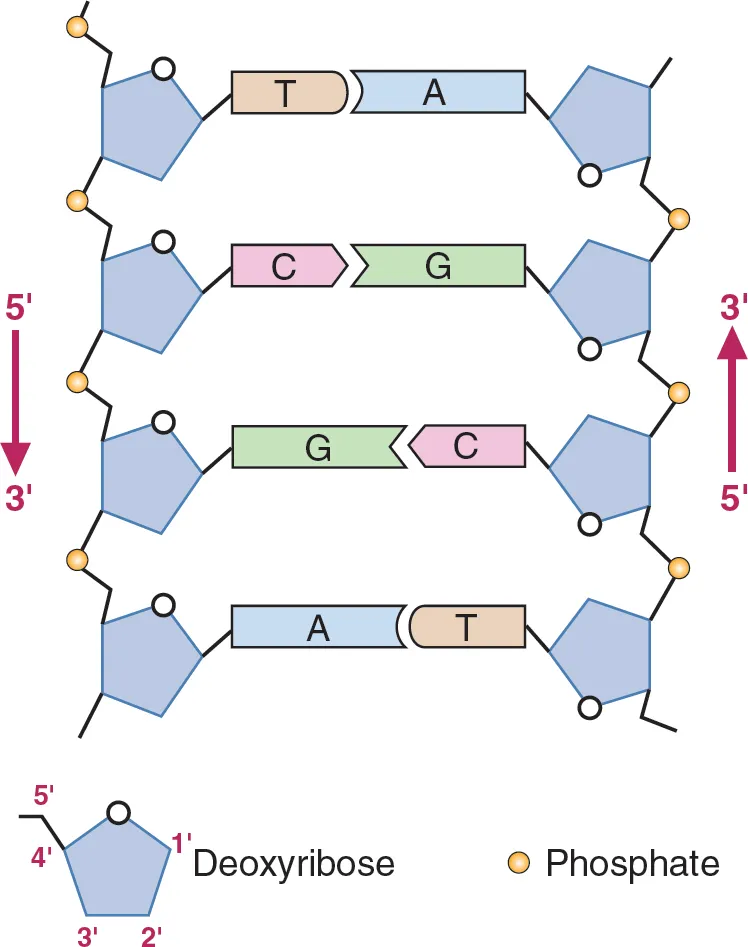
Why is the antiparallel structure of DNA so important?
The antiparallel nature of DNA is essential for DNA replication and other cellular processes. During reproduction, the two strands of the DNA double helix separate, and each strand serves as a template for synthesizing a new complementary strand. The antiparallel arrangement ensures that the new strands are synthesized in the correct orientation, with the 5′ end of one strand aligning with the 3′ end of the other.
The antiparallel structure allows DNA to form a stable double helix with the nitrogenous bases inside and the sugar-phosphate backbones outside. This configuration provides structural stability to the DNA molecule.







