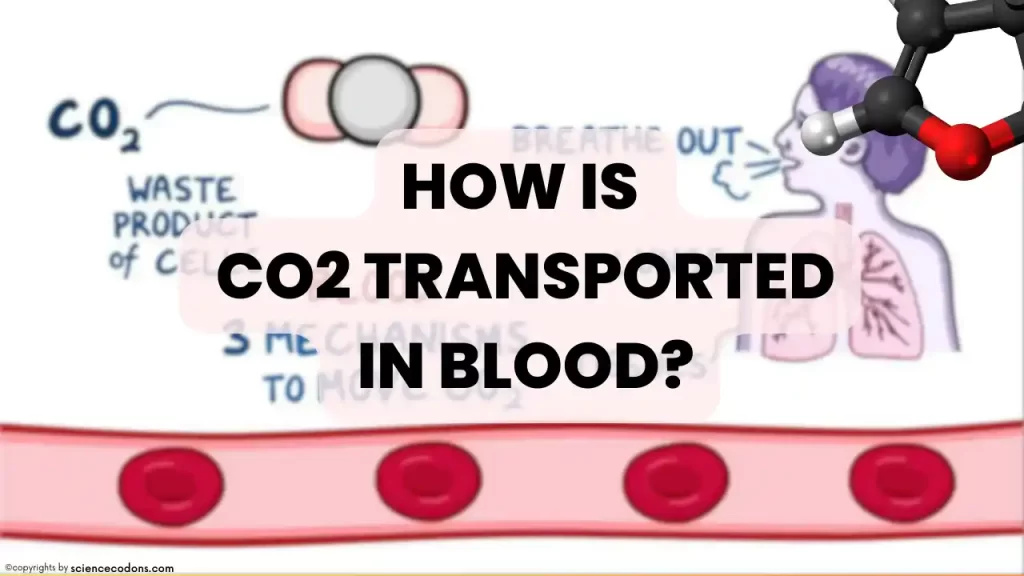
Carbon dioxide, unlike oxygen, has a high solubility in body fluids (plasma, cytoplasm, interstitial fluid, and cerebrospinal fluid). For this reason, a higher percentage of this gas is transferred between tissues in the form of a solution in blood compared to O2. There are three main mechanisms for transferring carbon dioxide from internal tissues to the lungs:
- Transporting CO2 in the form of a solution in plasma (about 7%)
- Conversion of CO2 to bicarbonate ions dissolved in blood (about 70%)
- Bound to hemoglobin (about 23%)
Transport of carbon dioxide gas by hemoglobin
Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood in three ways: dissolved in plasma, converted to bicarbonate ions, and bound to hemoglobin. Carbon dioxide reacts with the amino groups of lysine and arginine side chains. Each hemoglobin molecule can transport four CO2 molecules to the lungs, and about 23% of this gas is transported from the tissues to the lungs by binding to hemoglobin.
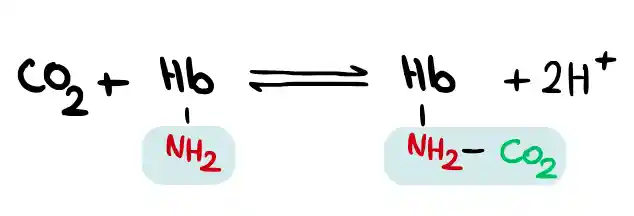
The mechanism of carbon dioxide binding to hemoglobin is that CO2 reacts with the free amino group (NH2-) in hemoglobin and combines with it. Hemoglobin that has CO2 bound to it is called carbaminohemoglobin.
Bohr and Haldane effects are two mechanisms that regulate the binding of carbon dioxide to hemoglobin. According to the Bohr effect, the tendency of hemoglobin to oxygen is inversely related to the concentration of carbon dioxide and the increase in pH. An increase in partial pressure or concentration of carbon dioxide increases the activity of the carbonic anhydrase enzyme, increases the formation of hydrogen ions (decreases pH), binds hydrogen ions to hemoglobin molecules, and consequently reduces the tendency of hemoglobin to oxygen.
How is carbon dioxide carried in the bloodstream?
Carbon dioxide is generally dissolved directly in the blood by about 7%. However, the main part of carbon dioxide (about 70%) is dissolved in the blood after being converted to bicarbonate ions. This ion is created by the combination of carbon dioxide with water molecules without the intervention of enzymes (very slow reaction) or with the participation of carbonic anhydrase enzyme (fast reaction).
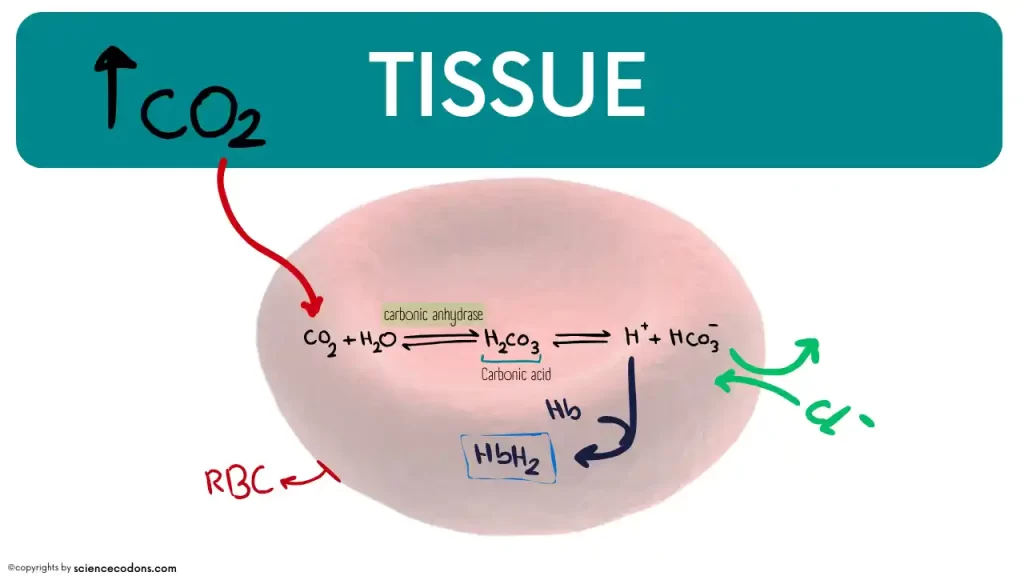
Metalloenzyme carbonic anhydrase (zinc element in the active site) produces carbon dioxide in a reversible reaction with water in many cells of the body, including red blood cells, distal tubule cells of the kidney, epithelial cells of the stomach, salivary gland secretory cells, and cerebrospinal fluid. The unstable compound carbonic acid immediately converts to bicarbonate ion and H+.
Reference:
CARBON DIOXIDE TRANSPORT IN BLOOD – Respiratory Physiology – Physiology 5th Ed. (doctorlib.info)