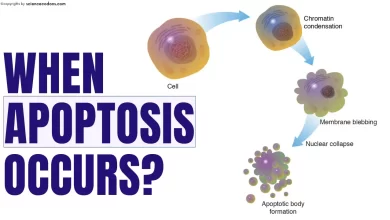
The term “apoptosis” was first introduced by researcher Kerr in 1972 to describe physiological cell death based on morphological changes and to distinguish it from necrosis.
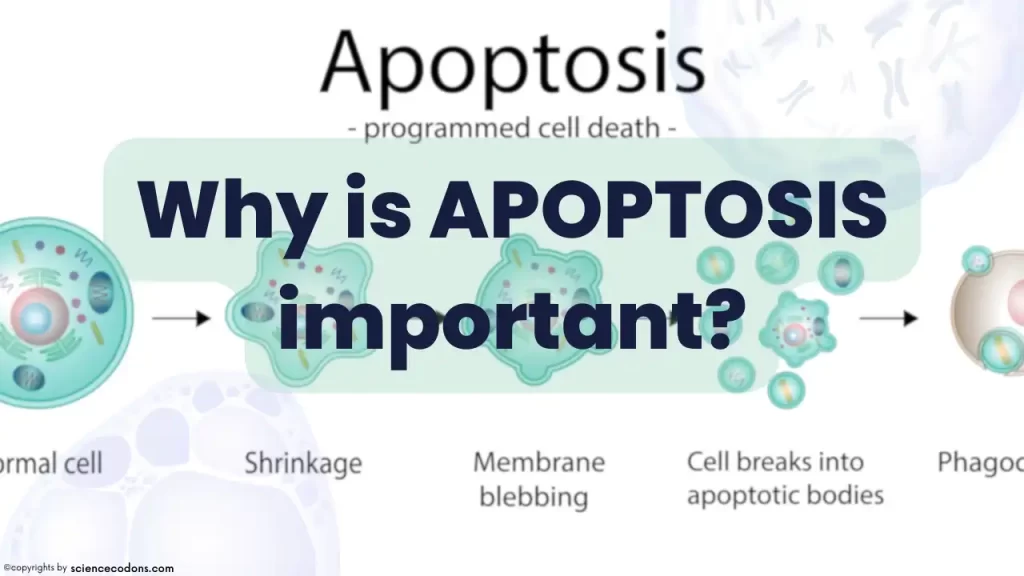
Apoptosis is a Greek word meaning “falling off” or “dropping off.” The terms “apoptosis” and “programmed cell death” are often used interchangeably. In contrast, others have referred to apoptosis as the most significant form of programmed cell death.
In this article, we will examine the importance of apoptosis in our body. Cellular apoptosis also plays an important role in human growth. For example, finger growth in the embryonic period begins with the tissues that fill the space between them, which are eliminated through apoptosis before birth.
The Role of Apoptosis in body homeostasis:
In adult multicellular animals, the number of body cells usually remains constant. The constancy of cell numbers in adults is due to the coordination of mitosis and programmed cell death. Cells create new cells through division. On the other hand, old, damaged, or excess cells are removed through apoptosis.
For further explanation, let’s consider an example. B lymphocytes proliferate and increase after encountering an antigen. These cells often succeed in removing foreign antigens by producing antibodies. However, after the foreign antigen is removed, the body does not need many B lymphocytes produced in response to it. So, what will happen to the stimulated B lymphocytes? The answer is very simple. These cells are removed by apoptosis after the antigen is removed. Of course, some B lymphocytes always remain as memory cells to defend the body against the same antigen in future encounters.
Apoptosis in development
Programmed cell death plays a very important role in tissue formation in animals and plants.
How is apoptosis involved in normal embryological development?
Research conducted on chicken embryos shows that during embryonic development, some body cells are selectively through apoptosis. This is also true for the embryos of other organisms. During the development and evolution of the embryo, apoptosis is tightly regulated. Different tissues utilize various signals to induce apoptosis in their surplus cells. For example, in birds, morphogenic bone proteins (BMPs) induce apoptosis in interdigital cells, leading to removing these cells. In Drosophila, steroid hormones induce apoptosis in some excess, aged, or damaged cells.