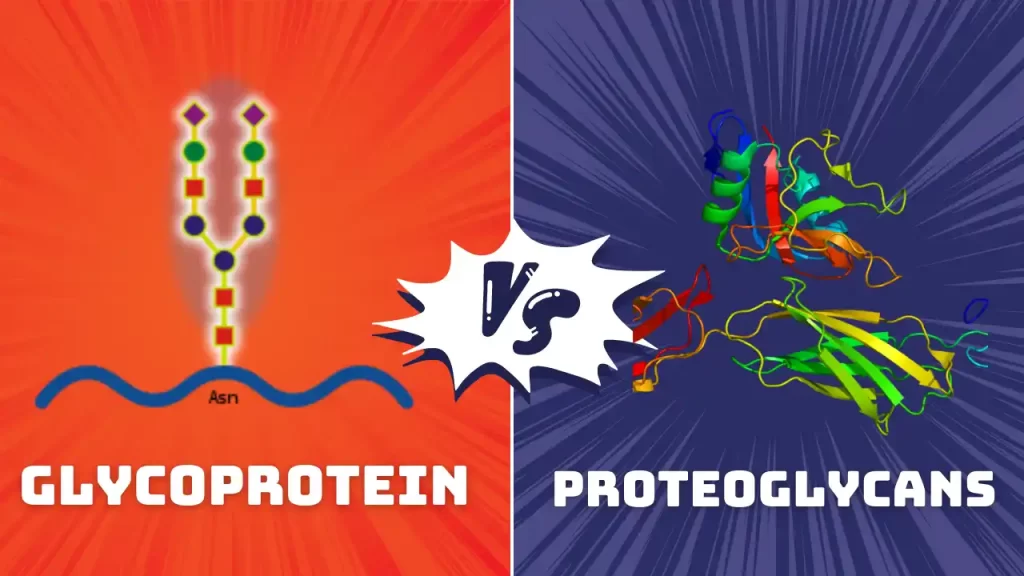
Glycoproteins and proteoglycans are two types of molecules that are composed of proteins and carbohydrates. They are both important components of the extracellular matrix, which is the network of molecules that surrounds and supports the cells in a tissue. However, glycoproteins and proteoglycans have different structures, functions, and locations in the body. In this post, we will explain the main differences between glycoproteins and proteoglycans and why they matter for biological processes.
What are Glycoproteins?
Glycoproteins are molecules with one or more short chains of sugars (oligosaccharides) attached to a protein backbone. The sugars are usually branched and can be either neutral or negatively charged. The attachment of sugars to proteins is called glycosylation, and it can occur either during or after the synthesis of the protein. Glycosylation can affect the folding, stability, activity, and interactions of the protein.
Glycoproteins are mainly found on the surface of cells, where they act as receptors, adhesion molecules, or antigens. Receptors are proteins that bind to specific molecules (ligands) and trigger a cellular response. For example, insulin receptors are glycoproteins that bind to insulin and regulate glucose uptake. Adhesion molecules are proteins that help cells stick to each other or to the extracellular matrix. For example, integrins are glycoproteins that mediate cell-matrix and cell-cell adhesion. Antigens are proteins that elicit an immune response when recognized by antibodies. For example, blood group antigens are glycoproteins that determine the compatibility of blood transfusions.
What are Proteoglycans?
Proteoglycans are molecules with one or more long chains of sugars (glycosaminoglycans or GAGs) attached to a protein core. The sugars are linear and negatively charged due to the presence of sulfate and uronic acid groups. The attachment of sugars to proteins is also called glycosylation, which usually occurs after synthesizing the protein. Glycosylation can affect the solubility, size, shape, and interactions of the protein.
Proteoglycans are mainly found in the extracellular matrix, providing structural support, hydration, and cushioning. They also modulate the activity and availability of growth factors, cytokines, and enzymes. Proteoglycans can be classified into different types based on the nature and number of the GAG chains. Some of the common types of proteoglycans are:
Aggrecan: This is the most abundant proteoglycan in cartilage, forming large aggregates with hyaluronic acid and link proteins. Aggrecan has many chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate chains, which give it a high water-binding capacity and resistance to compression.
Syndecan: This is a type of transmembrane proteoglycan that has both heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate chains. Syndecan acts as a co-receptor for various growth factors, such as fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
Decorin: This is a type of small leucine-rich proteoglycan that has a single chondroitin sulfate or dermatan sulfate chain. Decorin binds to collagen and regulates its fibril formation and organization. It also binds to growth factors, such as transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) and inhibits their signaling.
Heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG): This type of proteoglycan has heparan sulfate chains, which are highly sulfated and complex. HSPGs can be either transmembrane, such as syndecan and glypican, or secreted, such as perlecan and agrin. HSPGs involve many biological processes, such as cell adhesion, migration, differentiation, and angiogenesis.
Glycoprotein and proteoglycan examples
| Molecule | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Aggrecan | Proteoglycan | Provides hydration, mechanical strength, and shock absorption to cartilage |
| Perlecan | Proteoglycan | Supports basement membrane structure and regulates cell growth and differentiation |
| Versican | Proteoglycan | Modulates cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation in various tissues |
| Hemoglobin | Glycoprotein | Transports oxygen and carbon dioxide in red blood cells |
| Immunoglobulin G | Glycoprotein | Mediates immune response and protects against pathogens |
| Erythropoietin | Glycoprotein | Stimulates the production of red blood cells in bone marrow |
The main differences between glycoproteins & proteoglycans
The main differences between glycoproteins and proteoglycans are summarized in the table below.
| Feature | Glycoprotein | Proteoglycan |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrate units | Varied | Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) |
| Protein vs. carbohydrate | Protein dominant | Carbohydrate dominant |
| Function | Diverse | Structure and hydration |
| Examples | Antibodies, hormones, enzymes | Aggrecan, versican, decorin |
Why are the Differences Between Glycoproteins and Proteoglycans Important?
The differences between glycoproteins and proteoglycans are important because they reflect their different roles and functions in the body. Glycoproteins are mainly involved in cell-cell communication and recognition, while proteoglycans are mainly involved in tissue structure and integrity.
Both types of molecules are essential for the normal functioning of various biological systems, such as the immune system, the nervous system, the cardiovascular system, and the skeletal system. Moreover, the alterations or defects in glycoproteins or proteoglycans can lead to various diseases and disorders, such as cancer, inflammation, diabetes, arthritis, and congenital disorders.
Conclusion
Glycoprotein and proteoglycan are two important types of glycoconjugates with different structures, functions, and locations in the body. They play vital roles in various biological processes, such as cell-cell communication, tissue formation, and regulation of cell behavior. Understanding the difference between these two molecules can help us appreciate the diversity and complexity of life.
Reference:
- Essentials of Glycobiology (3rd Edition) by Ajit Varki et al.
- Lecture Notes on Glycobiology (Second Edition) by Hongbao Guo